Return to Section Header
There are two ways to extract metadata from documents in a case. Metadata can be extracted from documents during the import process. Using either LAW Electronic Discovery Loader or Turbo Import to import files into a case or by using the Batch Processing utility after documents have been imported into a case.
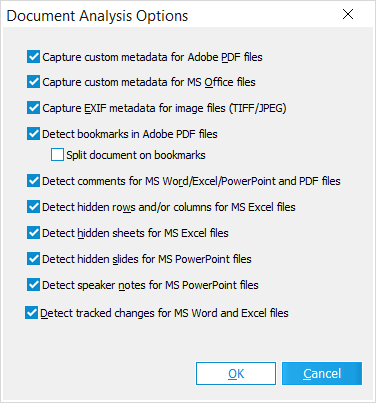
When extracting metadata, you can customize what type of metadata is extracted from the case files by selecting the metadata extraction options you want to apply. When importing documents, the metadata extraction options are defined on the Settings tab under the Metadata category in the LAW Electronic Discovery Loader dialog box. In the Batch Processing utility, metadata extraction options are defined in the Document Analysis Options dialog box.
For more information about extracting custom metadata during the import process, see Metadata.
The Document Processing/Analysis feature in the Batch Processing utility analyzes and extracts the metadata from the selected record set, based on the metadata extraction options selected in the Document Analysis Options dialog box. The Document Processing/Analysis feature in the Batch Processing utility also provides the option to split Adobe Acrobat PDF files by bookmarks into separate PDF files.
|
|
The PDF custom metadata extraction and the PDF split operation cannot be performed simultaneously or with other batch processing jobs in a batch. Each operation must be performed in a separate batch. |
•Detect comments for MS Word/Excel/PowerPoint and PDF Files - Assigns a Y to the HasComments field when detected.
•Detect hidden rows and/or columns for MS Excel files - Assigns a Y to the HasHiddenRow and/or HasHiddenColumn fields when detected.
•Detect hidden sheets for MS Excel files - Assigns a Y to the HasHiddenSheet field when detected.
•Detect hidden slides for MS PowerPoint files - Assigns a Y to the HiddenSlides field when detected.
•Detect speaker notes for MS PowerPoint files - Assigns a Y to the SpeakerNotes field when detected.
•Detect tracked changes for MS Word and Excel files - Assigns a Y to the HasTrackChanges field when detected.
![]() To Split PDF Files
To Split PDF Files
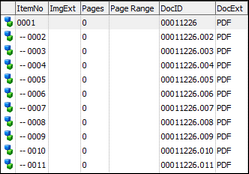
Adobe Acrobat PDF files can be split into separate PDF files bases on the original PDF file's bookmarks. Using the Document Processing/Analysis feature in the Batch Processing utility, you can have LAW identify the PDF files containing bookmarks, and then have these PDF files split, based on the PDF file's bookmarks. When a PDF file is split by bookmark, the original PDF file is deleted, and the PDF file containing the pages of the first bookmark becomes the parent file. The PDF files for the remaining bookmarks become the children of the first bookmark PDF file. For example: If a PDF file has 15 pages with 3 bookmarks (Bookmark 1 = pages 1-5, Bookmark 2 = pages 6-10, Bookmark 3 = pages 11-15), when the PDF file is split, the PDF file generated for bookmark 1 will be the parent file, and the PDF files generated for bookmarks 2 and 3 will be the child files.
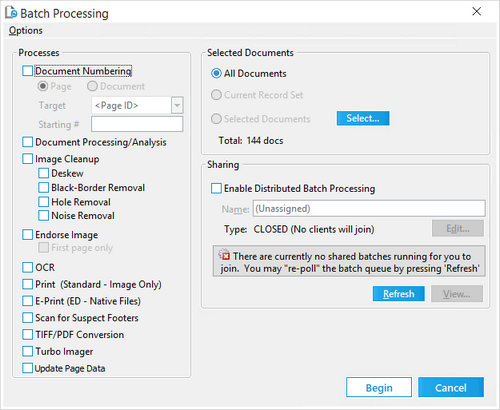
1. 2.Select the PDF files containing bookmarks that you want to split. For more information on selecting documents, see Selecting Documents for Processing.
3.Select the Document Processing/Analysis check box. 4.On the Options menu, click Document Analysis Options. Clicking Document Analysis Options opens the Document Analysis Options dialog box. 5.Select the Detect bookmarks in Adobe PDF files and Split document on bookmarks check boxes.
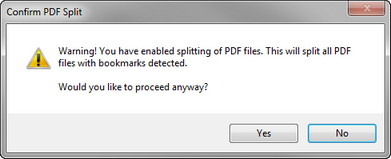
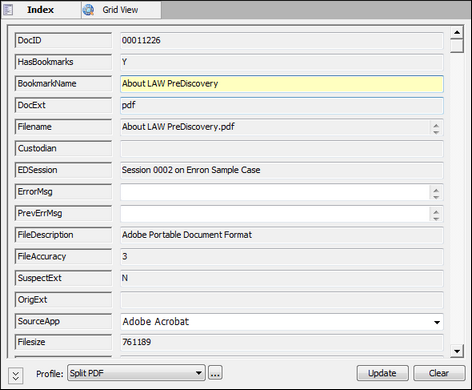
6.Click OK. Clicking OK opens the Confirm PDF Split message. 7.Click Yes. 8.Optionally, select the Enable Distributed Batch Processing check box and configure the session as needed. For more information on using distributed batch processing see Distributed Batch Processing. 9.Click the Begin button. When the batch process is completed, the Status dialog box is displayed. 10. When the batch process is completed the HasBookmarks field for the PDF files containing bookmarks is set to Y, and the BookmarkName field is populated with the name of the bookmark associated with the PDF file. If a bookmark name exceeds 251 characters, the bookmark name will be truncated.
|