After importing records, you may want to check for duplicates in Concordance Desktop. Duplicates are identified by comparing the content in selected fields. When Concordance Desktop finds duplicate records, Concordance Desktop tags each of the duplicate records. Give some forethought to what fields you want to use to check for duplicates. Before checking for duplicate records, make sure that there are not any records that were tagged in a previous duplicate check before you start the process again.
It is best practice to remove access to the Check for Duplicates menu command on the Tools menu from most users, except your advanced users.
When Concordance Desktop checks for duplicate records, Concordance Desktop only checks the records in the current query. If you want Concordance Desktop to check for duplicates in the entire database, be sure to run the Zero Query before checking for duplicates.
The duplication detection categorizes documents in three ways:
•When a record is unique, no tag is assigned to the record
•The first time a duplicate record appears, the Original tag, or its equivalent, is assigned to the record
•The subsequent times the duplicate record appears, the Duplicate tag, or its equivalent, is assigned to the records
To Check for Duplicate Records
1.Run a search query to locate the records you want to search for duplicate records.
i.For more information about searching, see Available search tools.
ii.When Concordance Desktop checks for duplicate records, Concordance Desktop only checks the records in the current query.
iii.If you want Concordance Desktop to check for duplicates in the entire database, be sure to run the Zero Query before checking for duplicates.
iv.For more information about the Zero Query, see Reviewing search queries.
2.On the Tools menu, click Check for duplicates.
i.Clicking Check for duplicates opens the Duplicate Detection dialog box.
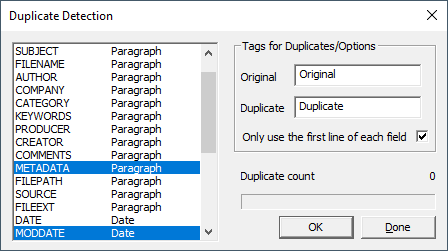
3.In the field list, click the fields you want Concordance Desktop to compare to identify duplicate records in the database's current query.
i.To select multiple fields, use SHIFT+click or CTRL+click.
ii.You can select as many fields as you want, but there is a limit of 245 characters that can be compared. Paragraph fields count as sixty characters.
iii.When you first open the Duplicate Detection dialog box, the Original field defaults to Original and the Duplicate field defaults to Duplicate. The Original field determines the name of the tag applied to the first record encountered in a duplicate record set, and the Duplicate field determines the name of the tag applied to the second record in a duplicate record set. You can modify the tags names in the Original and Duplicate fields to any tag name you want Concordance Desktop to use for duplicate records.
4.Before checking for duplicate records in the database, make sure that the database does not have any records that were already tagged with these tag names from a previous check for duplicate records.
5.If you selected a paragraph field in the field list, it is best practice to select the Only use the first line of each field check box.
i.If you do not want Concordance Desktop to compare all of the text in a field, up to the 245 character limit, clear the Only use the first line of each field check box.
6.Click OK to check for duplicate records.
i.The Duplicate count field displays the number of duplicate records found during the duplicate record check. Any duplicate records are tagged.
7.Click the Done button to close the Duplicate Detection dialog box.
8.To view the duplicate records, query the Original and Duplicate field tags.
i.For more information about querying tags, see Creating queries from tags.
Tallying Duplicates
You can also use the Tally feature in the Tally task pane to help identify duplicate records in the database. The Tally feature creates an itemized list of data values within a field, including the number of occurrences of each data value in the field.
For more information about the Tally feature, see Searching by tally.