Concordance search tools sort through vast amounts of information quickly using two search methodologies:
•Full-text Searching - Full-text searching is fast and produces results quickly because it searches for words based on index entries created when building the database. The index provides directions to words in the database dictionary and records are gathered for you to review based on search criteria.
•Relational Searches - Relational searches scan every word of every record in a database and take longer than full-text searches, because Concordance must read every record to locate your entries and does not use an index. Relational searches are great for locating dates and numbers, whereas full-text searches are optimal for word searches.
A Knowledge Based Articles on this subject can be found here:
•Searching Tips for Concordance (cloudnine.com)
•Simple Searches - Finding a Word or Phrase (cloudnine.com)
See Advanced Searching for more details about searching in Concordance.
When your Concordance administrator builds your record databases, the information is indexed for full-text searching capabilities. Once a record collection is indexed, a dictionary is created with additional filters that weed out unnecessary words, common English words, and even some punctuation, to improve search processing time. When reviewers make edits, redactions, or add new records to the database, the administrator must perform a reindex in Concordance to update your record collection. It is recommended to perform indexing when reviewers are not working in Concordance.
To more effectively execute full-text searches, it is important to understand the search concepts below.
Indexing and Re-indexing
When Concordance databases are built, the index and dictionary are generated from your document contents. The index contains location information for every word or character string in the database. The dictionary contains a list of every word or string of characters in your record collection, except words, punctuation, and/or field content your administrator specifically excludes from the dictionary.
A word is simply defined as any string of letters and/or numbers. Both airforce1 and ABC000001 could be words in the Concordance index.
Spaces break characters into multiple words, so a space between airforce and 1 would result in two separate words in the index.
In Concordance, updating the index is called a reindex. Reindexing updates the database dictionary and its corresponding index. Actively used databases need frequent reindexing to keep the index and dictionary entries current for searches.
Administrators are usually responsible for indexing or reindexing databases due to the sensitivity involved in running these processes. Concordance administrators must ensure that all data is reviewed and proper backups are made before indexing or reindexing a database.
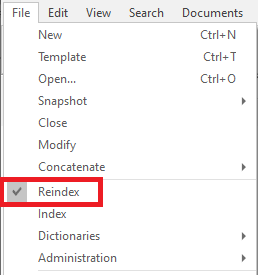
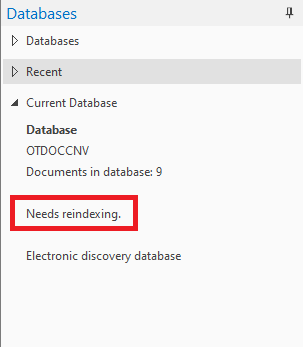
When updates have been made to a database and your database dictionary is no longer current with the latest updates, Concordance indicates that the database needs reindexing. On the file menu a check mark is displayed next to the Reindex command and Needs Reindexing is displayed in the Databases task pane under Current Database. If you do not have reindexing privileges, the Reindex command is not visible on the File menu.
Stopwords
Concordance comes with a pre-defined list of stopwords for each database. Stopwords are words that are automatically excluded from a database's index. The stopword list includes the most common words in the English language (for example: and, but, is, and the). Stopwords are words you normally would not search for. Eliminating these words from the index ensures that searches run faster and more efficiently. You can see the stopwords list for your database by going to File>Dictionaries>Stopword list.
Punctuation
For full-text searching, punctuation is not indexed. Concordance treats punctuation symbols as spaces when full-text searches are conducted. All punctuation is ignored, such as periods or quotations, as well as any symbols like currency and percentage.
You can search for words with punctuation if both of the following things are true:
•The punctuation character is defined by your administrator to be indexed in Concordance
•The punctuation is part of a string surrounded by two other characters
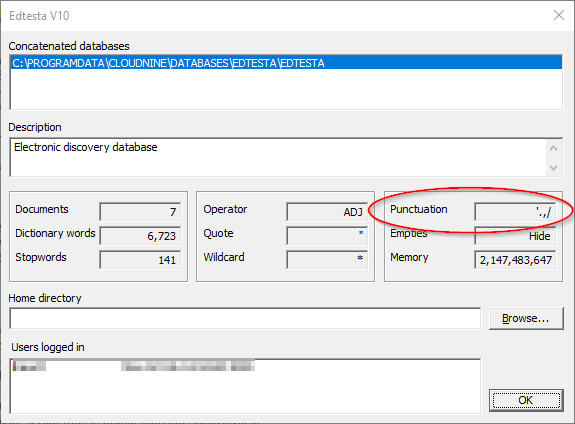
To see what punctuation your administrator defined to be indexed, go to File>Properties.
|
When using punctuation characters in your search term, at least one non-punctuation character needs to be inserted between the punctuation characters. For example: joe&i@email.com. Using two or more punctuation characters together will not work (joe&@email.com). |
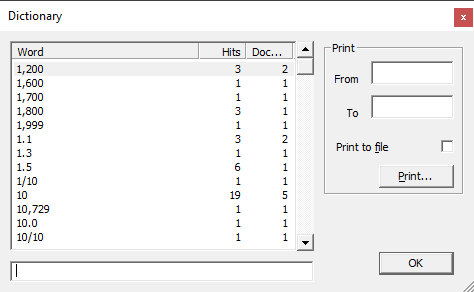
Dictionary
In Concordance, a word is any string of characters. A word can be a series of numbers or a combination of letters, numbers and even punctuation or symbols depending on your settings. You can view your dictionary by going to File>Dictionaries>Database Dictionary. The Dictionary dialog box provides a complete listing of all words included, the number of documents it appears in, and how many word hits there are.